GitHub Safe-Settings: Policy as Code
2025-02-11
Policy as Code
GitHub Settings
- Repository settings can easily be changed in the UI.
- Depending on collaborators permissions, they can change them too.
- Might turn something on/off and lose record.
- How to enforce for all repositories?
GitHub Safe-Settings
An app to manage policy-as-code and apply repository settings across an organisation.
- Create an
adminrepo (or an alternative of your choosing) within your organisation. - Add the settings for the
org,suborgs, andreposin YAML files. - Deploy and install the app. The
safe-settingscan also be run with GitHub Actions.
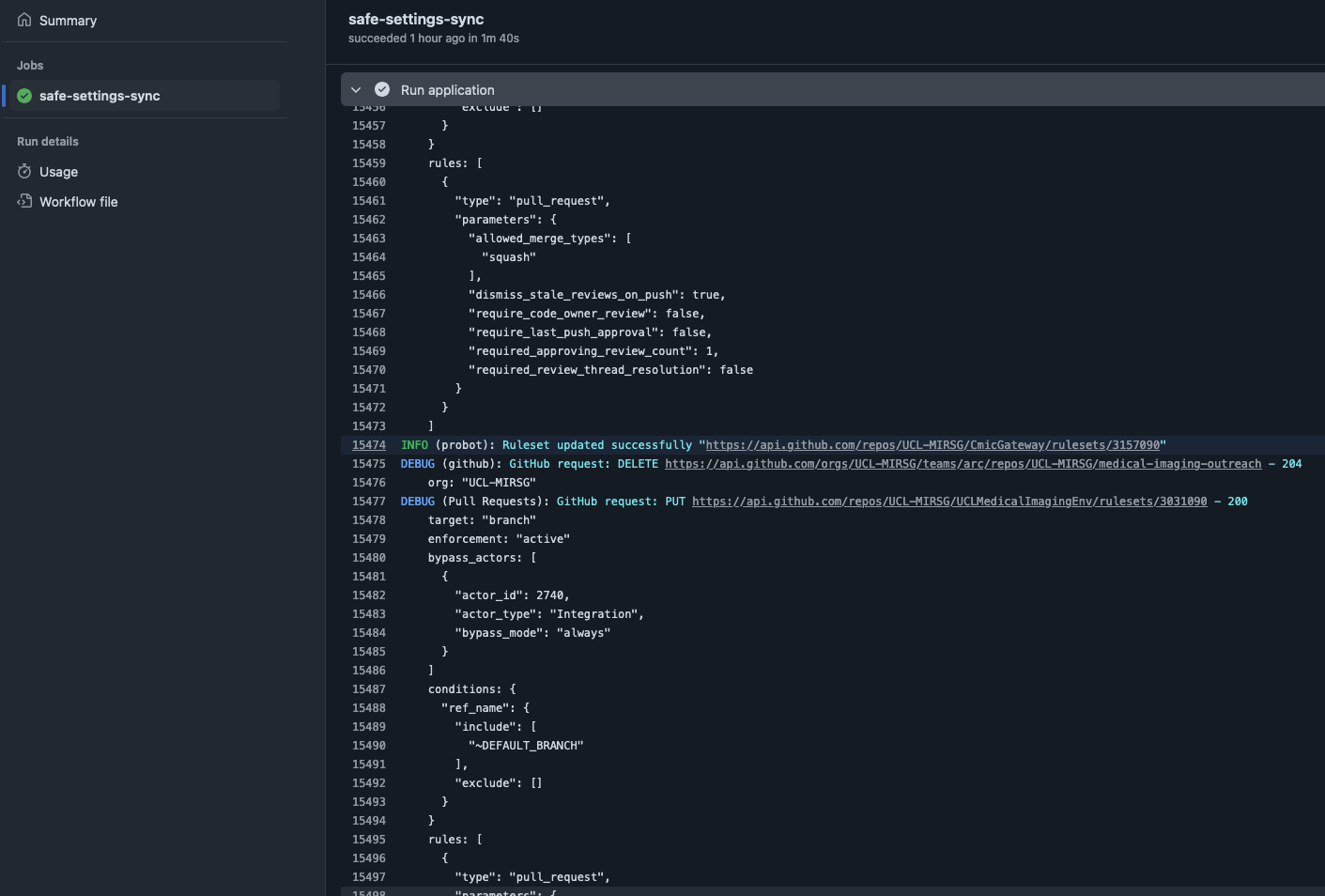
App Overview
- In
safe-settings, all the settings are stored centrally in anadminrepo within the organisation. Unlike the GitHub Repository Settings App, the settings files cannot be in individual repositories. - The settings in the default branch are applied. If the settings are changed on a non-default branch and a PR is created to merge the changes, the app runs in a
dry-runmode to evaluate and validate the changes. Checks pass or fail based on thedry-runresults.
- In
safe-settingsthe settings can have 2 types of targets:org- These settings are applied to the organisation.Org-targeted settings are defined in.github/settings.yaml. Currently, onlyrulesetsare supported asorg-targeted settings.repo- These settings are applied to repositories.
- For the
repo-targeted settings, there can be 3 levels at which the settings are managed:Org-level settings are defined in.github/settings.yaml.Suborglevel settings. Asuborgis an arbitrary collection of repos belonging to projects, business units, or teams. Thesuborgsettings reside in a YAML file for eachsuborgin the.github/suborgsfolder.Repolevel settings. They reside in a repo specific YAML in.github/reposfolder.
- It is recommended to break the settings into
org-level,suborg-level, andrepo-level units. This will allow different teams to define and manage policies for their specific projects or business units. WithCODEOWNERS, this will allow different people to be responsible for approving changes in different projects.
How it Works
Safe-settings is designed to run as a service listening for webhook events or as a scheduled job running on some regular cadence. It can also be triggered through GitHub Actions.
Events
The App listens to the following webhook events:
- push
- repository.created
- branch_protection_rule
- repository.edited
- repository.renamed
- pull_request.opened, pull_request.reopened, check_suite.requested
- repository_ruleset
- member_change_events
- member’, team.added_to_repository, team.removed_from_repository, team.edited
- custom_property_values
Deployment Settings
restrictedRepos:
# You can exclude certain repos from safe-settings processing
# If no file is specified, then the following repositories -
# 'admin', '.github', 'safe-settings' are exempted by default
exclude: ['^admin$', '^\.github$', '^safe-settings$', '.*-test']
# Alternatively you can only include certain repos
include: ['^test$']
configvalidators:
- plugin: collaborators
error: |
`Admin cannot be assigned to collaborators`
script: |-
console.log(`baseConfig ${JSON.stringify(baseconfig)}`)
return baseconfig.permission != 'admin'
overridevalidators:
- plugin: branches
error: |-
`Branch protection required_approving_review_count
cannot be overridden to a lower value`
script: |-
console.log(`baseConfig ${JSON.stringify(baseconfig)}`)
console.log(`overrideConfig ${JSON.stringify(overrideconfig)}`)
if (
baseconfig.protection.required_pull_request_reviews.required_approving_review_count
&&
overrideconfig.protection.required_pull_request_reviews.required_approving_review_count
) {
return
overrideconfig.protection.required_pull_request_reviews.required_approving_review_count
>=
baseconfig.protection.required_pull_request_reviews.required_approving_review_count
}
return true
- plugin: labels
error: |
Some error
script: |
return truePerformance
When there are 1000s of repos to be managed – and there is a global settings change – safe-settings will have to work efficiently and only make the necessary API calls.
The app also has to complete the work within an hour: the lifetime of the GitHub app token.
To address these constraints the following design decisions have been implemented:
Performance
Probotautomatically handlesrateandabuselimits.- Instead of loading all the repo contents from
.github/repos/*, it will selectively load the specific repo file based on whichreposettings has changed, or a subset of the repo files associated withsuborgsettings that has changed. The only time all the repo files will be loaded is if there is aglobalsettings file change.
Performance
- The PR check will only give a summary of errors and changes (providing the details of changes for 1000s of repos will error out).
- To ensure it handles updates to GitHub intelligently, it will compare the changes with the settings in GitHub, and will call the API only if there are
realchanges.
The Settings Files
The settings files can be used to set the policies at the org, suborg or repo level.
The following can be configured:
- Repository settings
- Default branch
- Topics
- Custom properties
- Teams and permissions
- Collaborators and permissions
- Issue labels
- Milestones
- Branch protections
- Autolinks
- Repository name validation
- Rulesets
- Environments
Things to Note
- Label colour can also start with
#, e.g.color: '#F341B2'. Make sure to wrap it with quotes. - Each top-level element under branch protection must be filled (for example:
required_pull_request_reviews,required_status_checks,enforce_adminsandrestrictions). If you do not want to use one of them you must set it tonull(see comments in the example above). Otherwise, none of the settings will be applied. - The precedence order is repository > suborg > org.
Example Configuration
./safe-settings/deployment.yaml
restrictedRepos:
# these repos are all archived and will cause the GHA to fail
# https://github.com/github/safe-settings/issues/443
exclude:
- ^AboutMeGateway$
- ^admin$
- ^ansible-collection-infrastructure-archive$
- ^ansible-collection-omero$
- ^ansible-collection-xnat$
- ^ansible-collection-xnat-archive$
- ^ansible-role-docker$
- ^ansible-role-firewalld$
- ^ansible-role-install-java$
- ^ansible-role-install-python$
- ^ansible-role-omero-web$
- ^ansible-role-postgresql$
- ^ansible-role-provision$
- ^ansible-role-selinux-utils$
- ^ansible-role-ssl-certificates$
- ^ansible-role-template$
- ^ansible-role-tomcat$
- ^catch-srv-plugin$
- ^chenies-mews-cleanup$
- ^cmic-xnat-plugin$
- ^comic100_dax_config$
- ^despiad_customizations$
- ^DevOps-Knowledge-Base$
- ^DicomAnonUtils$
- ^drc_cluster_dax_config$
- ^exo-flim$
- ^flimj-ops$
- ^flimj-ops-scripts$
- ^flimj-ui$
- ^flimlib$
- ^general_bulk_uploader$
- ^gif_extras$
- ^github-actions-maven$
- ^Infrastructure$
- ^LocalDevMedicalImagingEnv$
- ^MIRSE-Research-and-Documentation$
- ^mirsg-github-runner-docker$
- ^mirsg-harvester-terraform-modules$
- ^mirsg-xnat-user-documentation$
- ^module_segmentation$
- ^NCCID-clinical-datatype-for-Covid19-XNAT$
- ^NCCID-clinical-datatype-release$
- ^nccid-data-transfer$
- ^NiftyPipe$
- ^NiftyPipe-Data$
- ^nimg1946-legacy-scripts$
- ^nipype$
- ^omero-ansible-sandpit$
- ^OmeroInstaller$
- ^OmeroInstallerConfig$
- ^promis-omero-import$ # typos: ignore
- ^protocols$
- ^reimagine-bulk-uploader$
- ^SUMMITCOVIDGateway$
- ^test-gha-arc$
- ^ucl-xsync$
- ^uclh-gae-clinical-gateway$ # typos: ignore
- ^xnat$
- ^xnat-1946$
- ^xnat-azure-template-terraform$
- ^xnat-azure-terraform$
- ^XNAT-FTD$
- ^xnat-helper$
- ^xnat-setup$
- ^XnatInstaller$./safe-settings/organisation.yaml
autolinks:
- key_prefix: ARCMYS-
url_template: https://myservices-arc.uk.4me.com/requests/<num>
is_alphanumeric: false
repository:
allow_auto_merge: true
allow_merge_commit: false
allow_rebase_merge: false
delete_branch_on_merge: true
has_discussions: false
has_downloads: false
has_wiki: false
squash_merge_commit_message: PR_BODY
squash_merge_commit_title: PR_TITLE
teams:
- name: mirsg
permission: admin./safe-settings/suborgs/rulesets.yaml
suborgrepos:
- "*"
rulesets:
- name: Default
target: branch
enforcement: active
conditions:
ref_name:
include:
- ~DEFAULT_BRANCH
exclude: []
rules:
- type: deletion
- type: non_fast_forward # prevents force pushes
- name: Pull Requests
target: branch
enforcement: active
bypass_actors:
- actor_id: 2740 # Renovate Bot
actor_type: Integration
bypass_mode: always
conditions:
ref_name:
include:
- ~DEFAULT_BRANCH
exclude: []
rules:
- type: pull_request
parameters:
allowed_merge_types:
- squash
dismiss_stale_reviews_on_push: true
require_code_owner_review: false
require_last_push_approval: false
required_approving_review_count: 1
required_review_thread_resolution: false
- name: Status Checks
target: branch
enforcement: active
conditions:
ref_name:
include:
- ~DEFAULT_BRANCH
exclude: []
rules:
- type: required_status_checks
parameters:
do_not_enforce_on_create: false
required_status_checks:
- context: links
integration_id: 15368
- context: linting
integration_id: 15368
strict_required_status_checks_policy: falseGitHub Action
name: Safe Settings Sync
on:
push:
branches:
- main
pull_request:
paths:
- safe-settings/**
- .github/workflows/safe-settings.yaml
schedule:
- cron: 0 */4 * * *
workflow_dispatch: {}
concurrency:
cancel-in-progress: true
group: >-
${{ github.workflow }}-${{
github.event.pull_request.number || github.ref }}
jobs:
safe-settings-sync:
runs-on: ubuntu-slim
env:
SAFE_SETTINGS_VERSION: 2.1.14
SAFE_SETTINGS_CODE_DIR: .safe-settings-code
steps:
- name: Checkout source
uses: actions/checkout@11bd71901bbe5b1630ceea73d27597364c9af683 # v4
- name: Checkout GitHub Safe-Settings repository
uses: actions/checkout@11bd71901bbe5b1630ceea73d27597364c9af683 # v4
with:
path: ${{ env.SAFE_SETTINGS_CODE_DIR }}
ref: ${{ env.SAFE_SETTINGS_VERSION }}
repository: github/safe-settings
- name: Setup Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@39370e3970a6d050c480ffad4ff0ed4d3fdee5af # v4
with:
cache-dependency-path:
${{ env.SAFE_SETTINGS_CODE_DIR }}/package-lock.json
cache: npm
node-version-file: ${{ env.SAFE_SETTINGS_CODE_DIR }}/.nvmrc
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm install
working-directory: ${{ env.SAFE_SETTINGS_CODE_DIR }}
- name: Run application
run: npm run full-sync
working-directory: ${{ env.SAFE_SETTINGS_CODE_DIR }}
env:
ADMIN_REPO: .github
APP_ID: ${{ vars.SAFE_SETTINGS_APP_ID }}
BLOCK_REPO_RENAME_BY_HUMAN: false
CONFIG_PATH: safe-settings
DEPLOYMENT_CONFIG_FILE:
${{ github.workspace }}/safe-settings/deployment.yaml
ENABLE_PR_COMMENT: true
GH_ORG: ${{ vars.SAFE_SETTINGS_GH_ORG }}
GITHUB_CLIENT_ID: ${{ vars.SAFE_SETTINGS_GITHUB_CLIENT_ID }}
GITHUB_CLIENT_SECRET:
${{ secrets.SAFE_SETTINGS_GITHUB_CLIENT_SECRET }}
LOG_LEVEL: trace
PRIVATE_KEY: ${{ secrets.SAFE_SETTINGS_PRIVATE_KEY }}
SETTINGS_FILE_PATH: organisation.yamlRenovate Configuration
See https://paddyroddy.github.io/talks/renovate-automating-dependency-management for my earlier talk on Renovate.
{
$schema: "https://docs.renovatebot.com/renovate-schema.json",
extends: ["github>UCL-MIRSG/.github//renovate/default-config.json5"],
customManagers: [
{
customType: "regex",
description: "Update GitHub Safe-Settings version",
fileMatch: [".github/workflows/safe-settings.yaml$"],
matchStrings: ["SAFE_SETTINGS_VERSION:\\s(?<currentValue>.*)"],
depNameTemplate: "github/safe-settings",
datasourceTemplate: "github-releases",
},
],
}GitHub App
Creation
- Register new GitHub App.
- Give the app a unique name.
- Give the app a description.
- Give the app a homepage URL, e.g. https://github.com/github/safe-settings.
- Optionally disable
Expire user authorization tokens. - Disable webhook (assuming using GHA workflow).
- Give the following permissions:
Permissions
Repository
| Read-only | Read and write | |
|---|---|---|
| Actions | Administration | Environments |
| Metadata | Checks | Issues |
| Commit statuses | Pull requests | |
| Contents | Variables | |
| Custom properties |
Permissions
Organisation
| Read and write | Admin |
|---|---|
| Administration | Custom properties |
| Members |
Account
None
Next Steps
Where can this GitHub App be installed?Only on this account.- Create GitHub app.
- Generate a new client secret.
- Generate a private key.
- Optionally create a logo.

Next Steps
- Create the following environment variables:
secrets.SAFE_SETTINGS_GITHUB_CLIENT_SECRETsecrets.SAFE_SETTINGS_PRIVATE_KEYvars.SAFE_SETTINGS_APP_IDvars.SAFE_SETTINGS_GH_ORGvars.SAFE_SETTINGS_GITHUB_CLIENT_ID
- Install the app organisation wide.
Alternative Set Up
Follow the steps to register a GitHub App from a manifest.
default_events:
- branch_protection_rule
- check_run
- check_suite
- create
- custom_property_values
- member
- pull_request
- push
- repository
- repository_ruleset
- team
default_permissions:
actions: read
administration: write
checks: write
contents: write
environments: write
issues: write
members: write
metadata: read
organization_administration: write
organization_custom_properties: admin
pull_requests: write
repository_custom_properties: write
statuses: write
variables: write
name: Safe Settings
url: https://github.com/github/safe-settings
public: falseConclusions
- The ability to manage repository settings through version control.
- Can create and restrict what repositories are made.
- Can relax in the knowledge that new repositories will have settings that you expect.
- Quick even with many settings applied.
- Actively developed.
- Hosted on https://github.com/github.
- Can deploy in many different ways.
Demo
GitHub Safe-Settings: Policy as Code